what is necking in tensile test|tensile test simulation : Brand The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation or a failure. The tension or Compression test is primarily used to determine the relationship .
WEBAs REGRAS pra participar são simples, basta: Assinar YouCine Premium. É isso mesmo, nosso plano mais básico já te dá uma chance de ganhar! Mas se você adquirir nosso plano anual, são 12 chances de ganhar! É .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Here’s how to answer a question. It’s just 3 easy steps to answer a questio on the model train forum: Click on the ‘recent questions button’ at the top pf the page. Then click on the title of any question. Then just scroll down to see all of the question, the other answers, and the form for your own answer! .
Necking is thus predicted to start when the slope of the true stress / true strain curve falls to a value equal to the true stress at that point. This construction can be explored using the simulation below, in which the true .Necking: In engineering tensile tests, necking refers to the phenomenon where a material's cross-sectional area decreases under high stress. It's a vital phase that, in many . Necking starts when the plot of nominal stress against nominal strain reaches a maximum (plateau) – see Fig.3. This is not always easy to identify in terms of the strain at which it occurs, since it is commonly a rather .Definition. Necking is a phenomenon that occurs during the plastic deformation of materials, particularly metals, where a localized reduction in cross-sectional area happens as the .
Tensile Testing - Necking and Failure. With a brittle material, tensile testing may give an approximately linear stress-strain plot, followed by fracture (at a stress that may be affected .The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation or a failure. The tension or Compression test is primarily used to determine the relationship .
Tensile Testing - Necking and Failure. The uniaxial tensile test is the most commonly-used mechanical testing procedure. However, while it is simple in principle, there are several . What Does Necking Mean? Necking is a type of plastic deformation observed in ductile materials subjected to tensile stress. This deformation is characterized by a .
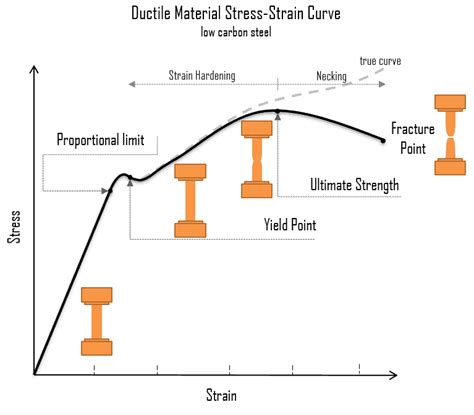
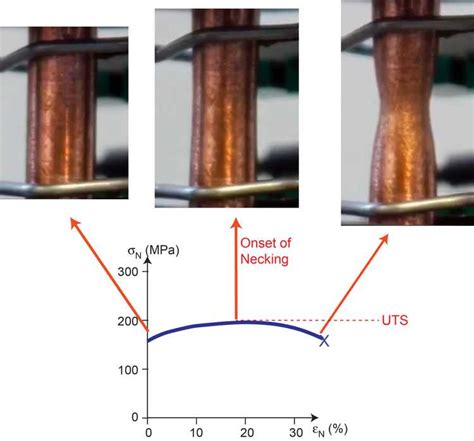
Ultimate Tensile Stress (UTS) and Ductility. It may be noted at this point that it is common during tensile testing to identify a “strength”, in the form of an “ultimate tensile stress” (UTS). This is usually taken to be the peak on the nominal stress v. nominal strain plot, which corresponds to the onset of necking. To predict the necking in the tensile test, a mechanically perfect, simple bar, finite element model is used and Hollomon’s constitutive law is utilized to describe the stress–strain curve. The approach is applied to a low-carbon steel. It has been shown that necking occurs at the exact point when the true strain of a specimen reaches the .We will look at a very easy experiment that provides lots of information about the strength or the mechanical behavior of a material, called the tensile test. What is a Tensile Test? Tensile Test Procedure; Tensile Tests of Composites; .
Necking in Tensile Testing: In tensile testing, which is a common practice in materials engineering, the necking stage is considered vital as it often signifies imminent material failure. The necking stage typically follows the yield point and strain hardening stage and marks the onset of the material's final phase towards fracturing.Static Tensile Test: In a static tensile test, the load is applied slowly and steadily over a long period of time. The rate of loading is slow enough that the material has time to fully respond to the applied stress, and the strain in the material is directly proportional to the applied stress. . Necking is a form of tensile deformation where . In summary, necking occurs during tensile testing of ductile materials due to the limiting uniform elongation and ultimate tensile strength. This is related to the conservation of mass and volume, observed in the Poisson effect, and the significant shearing in the necking area. The formation of necks is caused by the formation of micro-voids .
What is the complicating factor that occurs in a compression test that might be considered analogous to necking in a tensile test? - Barreling: The cross section at the interface is lesser than at the middle section due to friction between the test specimen and the compression testing machine surfaces.The term Tensile Testing Machine is widely used but actually the correct name these days for this type of materials testing equipment is a Universal Testing Machine because modern Tensile Testing Machines can be used to make many 100's of different tests not just tensile tests!
Tensile testing or Tensile Test is also known as Tension Test is a Destructive Test method and the most common type of . and hence the tensile specimen after fracture shows a flat surface without any necking in the fracture area. A brittle fracture occurs in both transgranular and intergranular. It is mainly observed in body-centered cubic .
After the tension has continued to rise steadily, a state is reached in which no further increase in force is required to extend the tensile test: the material continues to stretch evenly until an (initially slight) necking (waist formation) of the test specimen begins at one point. For uniaxial tensile test before necking, the stress components are zero, except the one in the tensile direction, denoted as σ 11. In this case, the tensile stress equals to the von Mises equivalent stress. The shear strain components (ε 12, ε 13, and ε 23) are zeros before necking in the uniaxial tensile test. The strain components in .The term "necking" is used in engineering and materials sciences to describe the localized reduction of cross-sectional area of a specimen under tensile load. Necking occurs when an instability in the material causes its cross-section to decrease by a greater proportion than the strain hardens when undergoing tensile deformation.
ultimate tensile strength on graph
Necking is a type of plastic deformation observed in ductile materials subjected to tensile stress. This deformation is characterized by a localized reduction in the cross-sectional area of the material, giving it a "V" or "neck" shape.
What is a tensile test?In the field of materials science and engineering, a tensile test is a widely used method to determine the mechanical properties of a material, specifically its response to tensile forces. It involves subjecting a specimen to an ever-increasing tensile load until it reaches its breaking point. By measuring the applied force and the resulting deformation . Figure 5 Necking of a tensile specimen o ccurring prior to . The tensile testing is carried out by applying longitudinal or axial load at a specific extension rate to a standard tensile specimen .Tensile Testing is a form of tension testing and is a destructive engineering and materials science test whereby controlled tension is applied to a sample until it fully fails. This is one of the most common mechanical testing techniques. It is .
Preparation of Specimen: Initially, the steel rod specimen is cleaned and gauge length is marked on it. The gauge length is calculated by the formula .. The gauge length can be marked on the specimen by punching tool. Range Calculation: A tensile stress value is assumed for which the maximum expected load capacity of the rod is calculated. From this, the range is calculated .
Tensile or tension testing is a fundamental and most commonly used test for the characterization of the mechanical behavior of materials. The test consists of pulling a sample of material and measuring the load and the corresponding elongation. . A triaxial state of stress applies in the necking area. A tensile hoop stress is developed around . A JIS tensile bar will generate a value a few percentage points higher than that generated from an ASTM tensile bar. Combine this with the normal test-to-test variability, and stamping performance may not coincide with your expectations. Some service centers will provide a copy of the certification document directly from the producing mill. Ultimate Tensile Stress (UTS) and Ductility. It may be noted at this point that it is common during tensile testing to identify a “strength”, in the form of an “ultimate tensile stress” (UTS).This is usually taken to be the peak on the nominal stress v. nominal strain plot, which corresponds to the onset of necking. Ductility is the measure of the strain during and after the moment of fracture. By analyzing the results of the tensile test, these three quantitative measurements can gauge the strength and durability of the specimen. Tensile Test Results. The results of a tensile test can give out valuable information regarding the substance used.
Both the load (stress) and the test piece extension (strain) are measured and from this data an engineering stress/strain curve is constructed, Fig.3.From this curve we can determine: a) the tensile strength, also known as the ultimate tensile strength, the load at failure divided by the original cross sectional area where the ultimate tensile strength (U.T.S.), σ max = P max /A 0, .Necking is a phenomenon that occurs during the plastic deformation of materials, particularly metals, where a localized reduction in cross-sectional area happens as the material is stretched. As the tensile stress increases, a point is reached where the material can no longer sustain uniform deformation, leading to this localized thinning. This process is critical in understanding .
Finally, the Forming Limit Curve (FLC) concept is used to judge how safe obtained strain distributions are in a real stamping or in the simulation of one. Although the FLC is the onset of necking, it is generally at higher strains than in a tensile test because in the latter a diffuse neck develops which cannot occur in sheet metal forming.
Tensile test results include ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, Young's modulus, ductility, and the strain hardening exponent. Specimen Geometry on Tensile Testing. . The necking region will occupy a much larger portion of the 1-in gauge length of Specimen B compared to the portion occupied on the 2-in gauge length of Specimen A. When .When a specimen goes through a tensile test, it reaches a level where the stress acting on it peaks, this leads to a decrease in the cross-section of the specimen in a localized region, this is called necking.The region in which the necking happens has the weakest cross-section, this is why necking takes place, and it's called the neck of the specimen.
tensile testing necking failure
Necking or plastic instability is a phenomenon that is unique to tensile testing. In ductile metals, necking starts at the maximum load in tension. A nonstrain-hardening, perfectly plastic material would become unstable in tension and start necking right in the beginning of the plastic yielding. Real metals, however, do show the phenomenon of .

Resultado da Ninfetinhas 🔞. 103 subscribers. View in Telegram. Preview channel. If you have Telegram, you can view and join Ninfetinhas .
what is necking in tensile test|tensile test simulation